내부 접근 : 객체 안에서 돌 때
외부 접근 : 외부에서 접근할 때
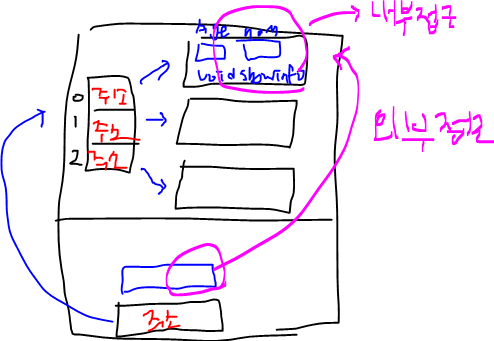
class Student {
// field : 필드, 멤버변수
int age;
String name;
// constructor
Student(int age, String name) {
this.age = age;
this.name = name;
}
// method
void showInfo() {
System.out.println("나이 : " + this.age);
System.out.println("이름 : " + this.name);
}
}
public class ArrayEx02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 객체 배열 : 1차원 배열
// 타입[] 배열명 = new 타입[길이];
Student[] smart = new Student[3];
smart[0] = new Student(20, "hong");
smart[1] = new Student(35, "park");
smart[2] = new Student(52, "lee");
// 1) 배열의 요소는 참조변수로 구성됨
// 1-1) 일반 for 문 : 내장변수 length
System.out.println("**** [배열의 요소] 일반 for 문 : 내장변수 length ****");
for (int i=0; i<smart.length; i++) {
System.out.println(smart[i]);
}
System.out.println();
// 1-2) 향상된 for 문
System.out.println("**** [배열의 요소] 향상된 for문 ****");
for (Student student: smart) {
System.out.println(student);
}
System.out.println();
// 과제 ========================================================================
// 2) 학생의 정보 출력 : showInfo() 호출
// 2-1) 일반 for 문 : 내장변수 length
System.out.println("**** [학생의 정보 출력] 일반 for 문 : 내장변수 length ****");
for (int i=0; i<smart.length; i++) {
smart[i].showInfo();
}
System.out.println();
// 2-2) 향상된 for 문
System.out.println("**** [학생의 정보 출력] 향상된 for문 ****");
for (Student student: smart) { // 배열에 저장된 값을 가져오는 거니까 타입은 요소의 타입과 일치해야함
student.showInfo();
}
System.out.println();
// 3) 모든 학생의 나이를 1 증가 (향상된 for 문으로 하기)
System.out.println("**** [모든 학생의 나이 1 증가] 향상된 for문 ****");
for (Student student: smart) {
student.age += 1;
student.showInfo();
}
System.out.println();
// 4) 학생의 정보 출력 : showInfo() 호출
System.out.println("**** age 값 변경 후 showInfo() 실행 ****");
for (Student student: smart) {
student.showInfo();
}
}
}'Language > JAVA' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 002. 자바 활용 백엔드 개발 기초 (0) | 2024.04.12 |
|---|---|
| JAVA 프로그래밍 기초 연습 문제 - Parameter (0) | 2024.04.09 |
| JAVA 프로그래밍 기초 연습 문제 - 2차원 배열 생성과 동시에 초기화하기 (0) | 2024.04.08 |
| JAVA 프로그래밍 기초 연습 문제 - 중첩된 for문과 향상된 for문 (0) | 2024.04.08 |
| JAVA 프로그래밍 기초 연습 문제 - constructor 와 setter 의 차이 (1) | 2024.04.08 |
